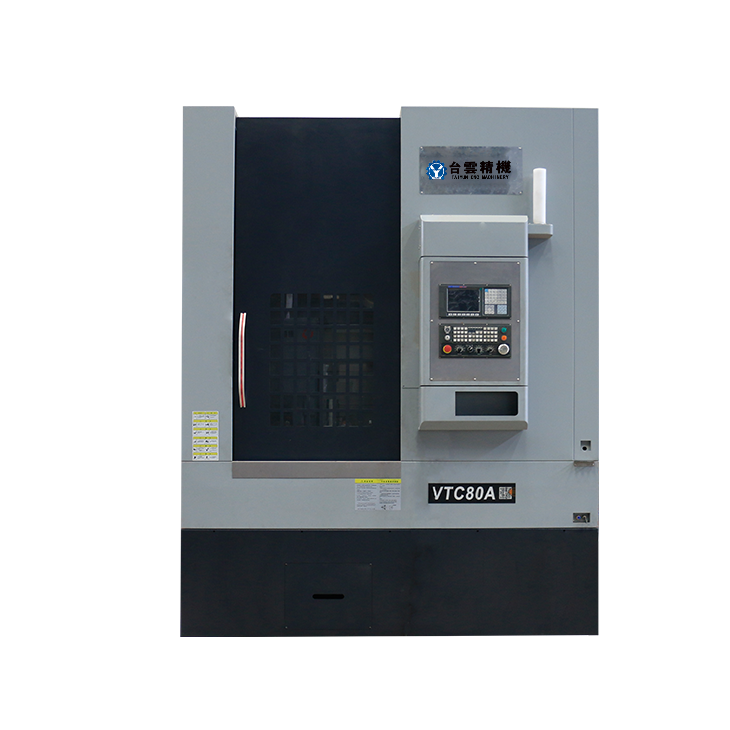
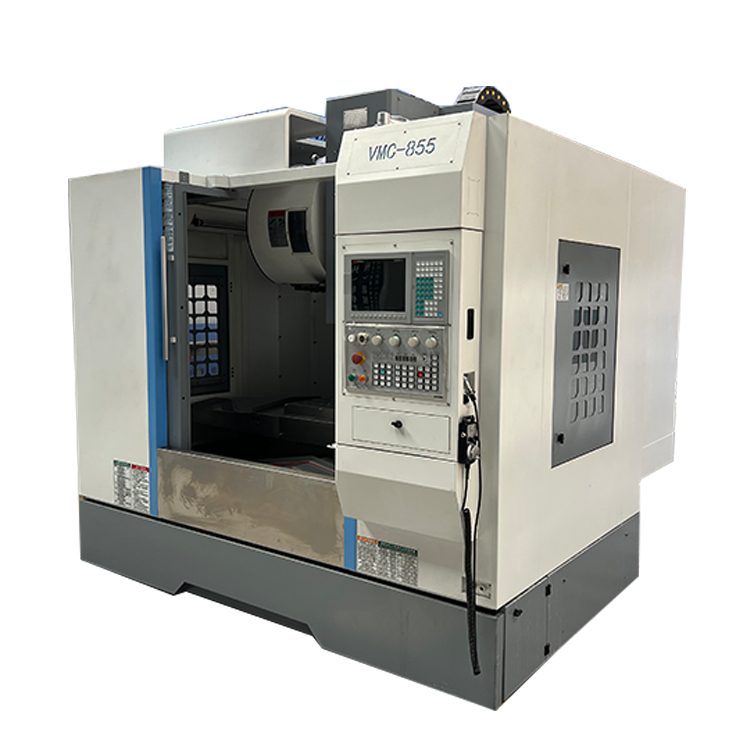
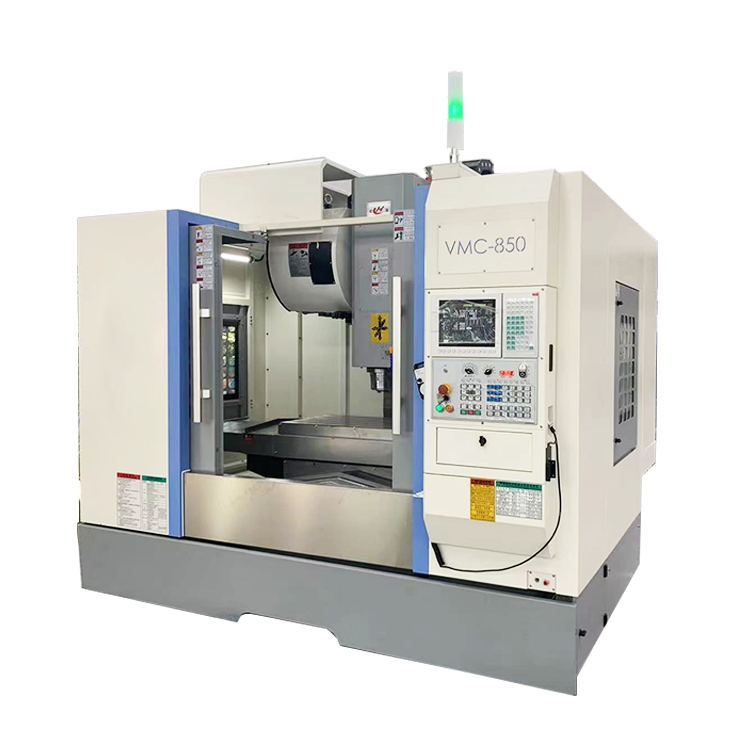
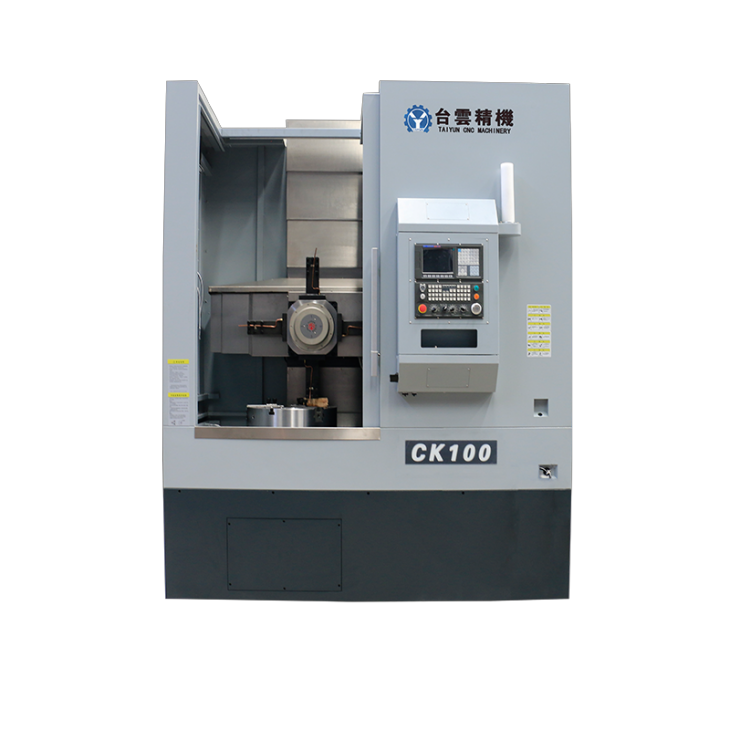
- Recommended news
-
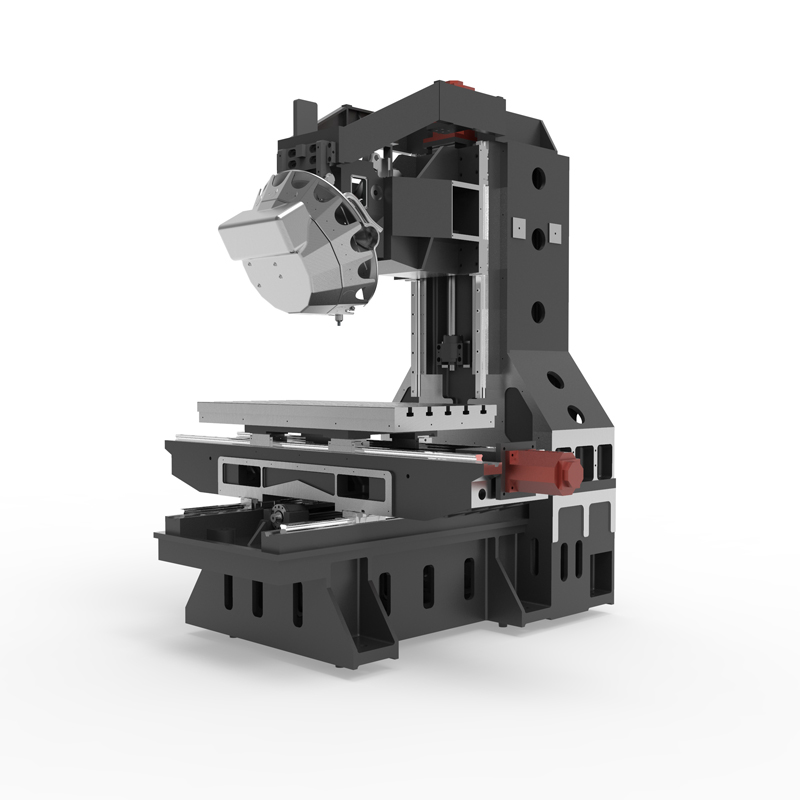
System composition of CNC horizontal machining center
2024-06-18
-
A method to solve the problem of spindle shaking in CNC lathes
2024-06-15
-
In which industry is the most widely used CNC vertical lathe?
2024-06-04
-
How to clamp the workpiece on a CNC vertical lathe?
2024-05-29
-
CNC milling machine machining center commonly used accessories
2024-05-25
-
Steps for adjusting the turret of a CNC vertical lathe
2024-05-22
Automated machining center
Automated machining center refers to mechanical equipment that uses a computer control system to automatically perform processing tasks....
Automated machining center refers to mechanical equipment that uses a computer control system to automatically perform processing tasks. The automated machining center combines CNC technology, sensor technology and automation technology to achieve high-precision and high-efficiency processing operations. Here is some important information about automated machining centers:
1. Working principle: The automated machining center controls each axial movement through the pre-programmed processing program and the CNC system to drive the tool or workpiece to perform precise processing operations. Automated machining center sensors are used to monitor the processing status and workpiece position in real time to ensure processing accuracy and quality.
2. Equipment composition: Automated machining centers usually include machine tool bodies, CNC systems, tool magazines/tool changing devices, workpiece clamping devices, automated feeding devices, lubrication systems, cooling systems and other components. Among them, the automated feeding device can realize automatic loading and unloading of workpieces and improve production efficiency.
3. Processing capabilities: The automated machining center has multi-axis control capabilities and can process complex parts, such as curved surface processing, hole processing, thread processing, etc. It has high precision and repeatability and is suitable for industries that require high processing accuracy, such as aerospace, automobile manufacturing, etc.
4. Advantages: Automated machining centers can realize automation and digitization of the production process, reduce manual operations, reduce labor costs, and improve production efficiency and product quality. At the same time, automated machining centers can flexibly adjust processing procedures to meet the needs of multi-variety and small-batch production.
5. Application fields: Automated machining centers are widely used in aerospace, automobile manufacturing, mold manufacturing, electronic equipment manufacturing and other industries, especially in areas with high processing requirements for complex parts.
Generally speaking, automated machining centers represent the development trend of modern manufacturing and are one of the important equipment to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure product quality. With the continuous development of technology, the application scope and functions of automated machining centers are also constantly expanding and improving.
| Specifications/model | unit | VT640A/B | VT840A/B | VT1050A/B | VT1350A/B | VT1650A/B |
| Work content | ||||||
| working desk size | MM | 700×400 | 1000×400 | 1100×500 | 1300×500 | 1700×500 |
| X-axis travel (left and right) | MM | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1300 | 1600 |
| Y-axis travel (front and rear) | MM | 400 | 400 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Z-axis travel (up and down) | MM | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 |
| Distance from spindle nose to work surface | MM | 100-500 | 100-500 | 100-500 | 100-500 | 100-500 |
| Z-axis heightening (optional) | MM | 300-650 | 300-650 | 300-650 | 300-650 | 300-650 |
| Maximum load of workbench | KG | 350 | 350 | 550 | 550 | 550 |
| Spindle specifications (Type A) | ||||||
| Spindle bore taper | BT | BT30 | BT30 | BT30 | BT30 | BT30 |
| Spindle structure | / | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection |
| Spindle speed | RPM | 20000 | 20000 | 20000 | 20000 | 20000 |
| Spindle horsepower | KW | 3.7/5.5 | 3.7/5.5 | 3.7/5.5 | 3.7/5.5 | 3.7/5.5 |
| Spindle specifications (type B) | ||||||
| Spindle structure | / | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection | direct connection |
| Spindle bore taper | BT | BT40 | BT30 | BT30 | BT30 | BT30 |
| Spindle speed | RPM | 12000 | 12000 | 12000 | 12000 | 12000 |
| Spindle horsepower | KW | 7.5/11 | 7.5/11 | 7.5/11 | 7.5/11 | 7.5/11 |
| Feed content | ||||||
| G00 rapid feed | M/MIN | 48/48/48 | 48/48/48 | 48/48/48 | 48/48/48 | 48/48/48 |
| G01 cutting feed | MM/MIN | 1-10000 | 1-10000 | 1-10000 | 1-10000 | 1-10000 |
| Servo motor specifications | RPM | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Motor connection method | / | Direct | Direct | Direct | Direct | Direct |
| XY/Z ball screw specifications | MM | 28/3216 | 28/3216 | 32/4016 | 32/4016 | 32/4016 |
| X-axis rail specifications | MM | 30Ball | 30Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball |
| Y axis rail specifications | MM | 30Ball | 30Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball |
| Z axis rail specifications | MM | 35Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball | 35Ball |
| Precise shaft positioning | MM | ±0.005/300 | ±0.005/300 | ±0.005/300 | ±0.005/300 | ±0.005/300 |
| Repeatable positioning precision | MM | ±0.003/300 | ±0.003/300 | ±0.003/300 | ±0.003/300 | ±0.003/300 |
| Minimum move value | MM | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Tool magazine system | ||||||
| Tool magazine structure | PCS | Clamp type | Clamp type | Clamp type | Clamp type | Clamp type |
| Servo tool magazine capacity | T | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| Tool changing time T-T | MIN | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Maximum tool capacity | KGS | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Oil and gas pressure system | ||||||
| air pressure | KG | 6.5-8 | 6.5-8 | 6.5-8 | 6.5-8 | 6.5-8 |
| Lubricating oil capacity | L | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| battery capacity | KW | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| coolant capacity | L | 220 | 220 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Form factor | ||||||
| Machine weight (approx.) | KG | 3200 | 3600 | 5500 | 6800 | 8000 |
| Machine length (front and rear) | MM | 1800 | 2000 | 2600 | 3400 | 4200 |
| Machine width (left and right) | MM | 1600 | 1600 | 2400 | 2400 | 2400 |
| Machine height (maximum) | MM | 2500 | 2500 | 2700 | 2700 | 2700 |
| Machine height (minimum) | MM | 2100 | 2100 | 2300 | 2300 | 2300 |
| Chip removal method | / | backlash | backlash | backlash | backlash | backlash |

 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Россия
Россия  Français
Français España
España عرب .
عرب .  Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch भारत
भारत Нидерланды
Нидерланды